|
DGtal
0.6.devel
|
|
DGtal
0.6.devel
|
This part of the manual describes how to import and export images and main DGtal objects from/to various formats.
In DGtal, file readers and writers are located in the "io/readers/" and "io/writers/" folders respectively. Most of them are dedicated to image format import/export but some other DGtal data structures can have such tools (e.g. point set/mesh readers).
Before going into details, let us first present an interesting tool for image visualisation or image export: predefined colormaps to convert scalars or to (red,green,blue) triplets.
Colormap models satisfy the CColormap concept. For short, a colormap is parametrized by a scalar value template type (Value). When constructed from two min and max values (of type Value), the colormap offers an operator returning a DGtal::Color for each value v in the interval [min,max].
For example, RandomColorMap returns a random color for each value v. More complex colormaps (GradientColorMap, HueShadeColorMap, ...) offer better colormap for scientific visualisation purposes.

In some situations, we may have to convert colors into scalar values (see below). In this case, basic conversion functors are available in the DGtal::BasicColorToScalarFunctors namespace. For example, you would find in this namespace a DGtal::BasicColorToScalarFunctors::RedChannel converter or a DGtal::BasicColorToScalarFunctors::MeanChannels converter.
Hence, to implement a functor taking values and returning the red channel of a colormap, you just have to compose the two functors with the help of the Composer:
We first detail import/export format for DGtal images. Please refer to Images for details on images in DGtal and their associated concepts. First of all:
Hence, for image writers, some functors may return a DGtal::Color or a scalar value depending on the writer.
| Dimension | Name | Description | Functor requirements | Class name | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | PGM | Grayscale netpbm image format | the functor should return an unsigned char | PGMWriter | http://netpbm.sourceforge.net/ |
| PPM | Color netpbm image format | the functor should return a DGtal::Color | PPMWriter | http://netpbm.sourceforge.net/ | |
| 3D | PGM3D | Grayscale netpbm image format | the functor should return an unsigned char | PGMWriter | |
| PPM3D | Color netpbm image format | the functor should return a DGtal::Color | PPMWriter | ||
| Vol | Volumetric file format | the functor should return an unsigned char | VolWriter | Simplevol project, http://liris.cnrs.fr/david.coeurjolly | |
| Longvol | Volumetric file format (long) | the functor should return a DGtal::uint64_t | LongvolWriter | Simplevol project, http://liris.cnrs.fr/david.coeurjolly | |
| nD | Raw8 | raw binary file format on 8bits | the functor should return an unsigned char | RawWriter |
For scalar value format (PGM, Vol, Longvol, Raw, ...), the associated template class have a default functor type. Hence, if you just want to cast your image values to the file format value type (e.g. "unsigned char" for Vol), do not scpecify any functor.
| Dimension | Name | Description | Class name | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | PGM | Grayscale netpbm image format | PNMReader | http://netpbm.sourceforge.net/ |
| any Magick format | Any file format in the GraphicsMagick library | MagickReader | with WITH_MAGICK build flag, http://www.graphicsmagick.org/ | |
| 3D | PGM3D | Grayscale netpbm image format | PNMReader | |
| Vol | Volumetric file format | VolReader | Simplevol project, http://liris.cnrs.fr/david.coeurjolly | |
| Longvol | Volumetric file format (long) | LongvolReader | Simplevol project, http://liris.cnrs.fr/david.coeurjolly | |
| nD | Raw8 | raw binary file format on 8bits | RawReader |
The static class PointListReader allows to read discrete points represented in simple file where each line represent a single point.
The static class MeshReader allows to import MeshFromPoints from OFF or OFS file format. Actually this class can import surface mesh (MeshFromPoints) where faces are potentially represented by triangles, quadrilaters and polygons. Notes that MeshFromPoints can be directly displayed with Viewer3D.
The mesh importation can be done automatically from the extension file name by using the "<<" operator. For instance (see. Import 3D mesh from OFF file ):
You can also export a MeshFromPoints object by using the operator (">>"). Notes that the class Display3D permits also to generate a MeshFromPoints which can be exported (see. Export 3D mesh in OFF and OBJ format).
Importing and visualizing a digital set from a vol file can be done in few code lines. (see. file digitalSetFromVol.cpp).
First we select the Image type with int:
Then the initial image is imported:
Afterwards the set is thresholded in ]0,255[:
Then you will obtain the following visualisation:
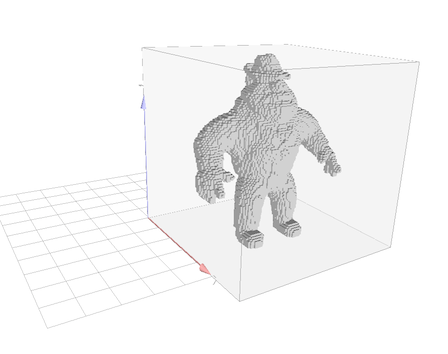
The example digitalSetFromPointList.cpp shows a simple example of 3d set importation:
We can change the way to select the coordinate field:
You may obtain the following visualisation:
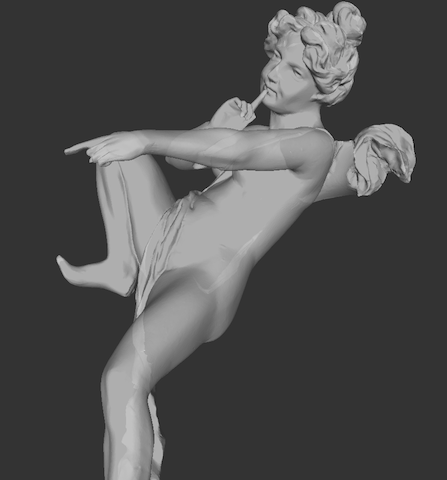
The following example (meshFromOFF.cpp ) shows in few lines how to import and display an OFF 3D mesh. Add the following headers to access to OFF reader and Viewer3D:
then import an example ".off" file from the example/sample directory:
Display the result:
You may obtain the following visualisation:

You can also import large scale mesh, like the one of classic Angel scan ( available here: http://www.cc.gatech.edu/projects/large_models/ )

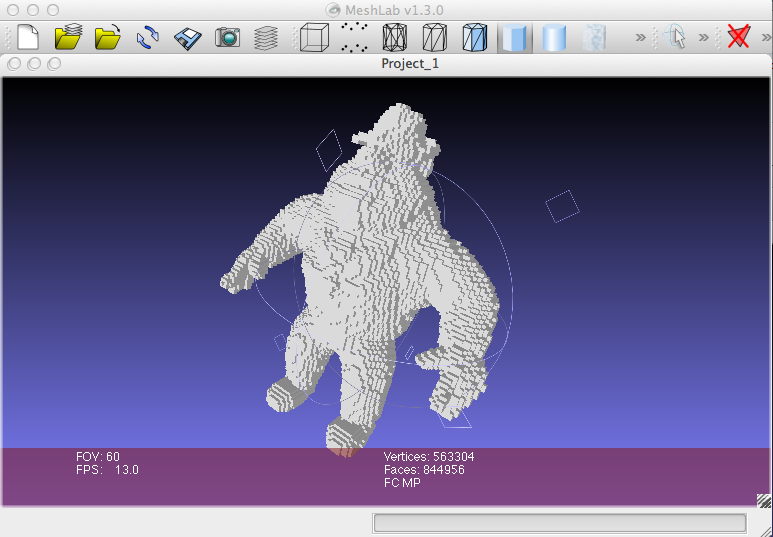
The following example (display3DToOFF.cpp shows in few lines how to export in OFF format a MeshFromPoints object. This object will be exported from a Display3D object (see. display3DToOFF).
Notes that the export can also be done in two steps:
The resulting mesh can be visualized for instance by using meshlab;
This code can be useful if you want to generate illustrations in the U3D format. For instance by using the U3D/PDF export from MeshLab or JReality ( www3.math.tu-berlin.de/jreality/). You can for instance generate some exports in pdf like this example:
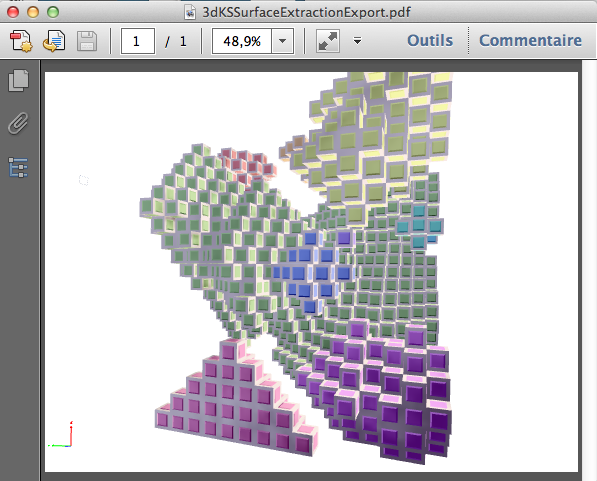
(see this pdf file: https://liris.cnrs.fr/dgtal/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/3dKSSurfaceExtractionExport.pdf )
 1.8.1.1
1.8.1.1