Version 20131215 (Dec 15, 2013)
Pascal Getreuer, getreuer@cmla.ens-cachan.fr, CMLA, ENS Cachan
Please cite IPOL article "A Survey of Gaussian Convolution Algorithms" if you publish results obtained with this software. This software was written by Pascal Getreuer and is distributed under the terms of the GPL or simplified BSD license. Future releases and updates will be posted at http://dev.ipol.im/~getreuer/code/.
Overview
This C source code accompanies with Image Processing On Line (IPOL) article "A Survey of Gaussian Convolution Algorithms" by Pascal Getreuer. The article and online demo can be found at http://www.ipol.im. This work surveys algorithms for computing and efficiently approximating Gaussian convolution,
![\[ u(x)=(G_\sigma*f)(x):=\int_{\mathbb{R}^d}G_\sigma(x-y)f(y)\,dy,\]](form_8.png)
where f is the input signal, u is the filtered signal, and 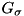 is the Gaussian with standard deviation
is the Gaussian with standard deviation 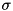 ,
,
![\[ G_\sigma(x)=(2\pi\sigma^2)^{-d/2}\exp\left(-\frac{\lVert x \rVert_2^2}{2\sigma^2}\right). \]](form_11.png)
Algorithms
- FIR Gaussian convolution
- DCT-based Gaussian convolution
- Box filter Gaussian convolution
- Extended box filter Gaussian convolution
- Stacked integral images Gaussian convolution
- Alvarez-Mazorra Gaussian convolution
- Deriche Gaussian convolution
- Vliet-Young-Verbeek Gaussian convolution
License
This code is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under, at your option, the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version, or the terms of the simplified BSD license.
You should have received a copy of these licenses along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/ and http://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.html.
Compilation
A makefile makefile.gcc is included for compilation with GCC on Linux or MinGW+MSYS on Windows.
Compiling requires the FFTW3 Fourier transform library (libfftw) http://www.fftw.org/. For supporting additional image formats, the programs can optionally be compiled with libjpeg, libpng, and/or libtiff. Windows BMP images are always supported.
Please see the readme for more detailed instructions.
Use
gaussian_demo
The gaussian_demo.c program applies 2D convolution using any algorithm on an image.
- Syntax
gaussian_demo [options] <input> <output>
where <input> and <output> are BMP files (JPEG, PNG, or TIFF files can also be used if the program is compiled with libjpeg, libpng, and/or libtiff).
The algorithm and Gaussian standard deviation are configured through the command line options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-a <algo> | algorithm to use, choices listed below |
-s <number> | sigma, standard deviation of the Gaussian |
-K <number> | specifies number of steps (box, ebox, sii, am) |
-t <number> | accuracy tolerance (fir, am, deriche, vyv) |
Specified with the -a <algo> option, choices of algorithm are
<algo> | Description |
|---|---|
fir | FIR approximation, tol = kernel accuracy |
dct | DCT-based convolution |
box | box filtering, K = # passes |
ebox | extended box filtering, K = # passes |
sii | stacked integral images, K = # boxes |
am | Alvarez-Mazorra using regression on q, K = # passes |
deriche | Deriche recursive filtering, K = order |
vyv | Vliet-Young-Verbeek recursive filtering, K = order |
gaussian_bench
The gaussian_bench.c program tests the speed, accuracy, and impulse response of any of the Gaussian convolution algorithms.
- Syntax
gaussian_bench [bench type] [options]
The program can run three different bench types:
| Bench type | Description |
|---|---|
speed | measure computation time |
accuracy | measure 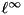 operator norm error operator norm error |
impulse | compute impulse response, written to bench.out |
The algorithm and Gaussian standard deviation are specified using the same options as with the gaussian_demo program. Additionally, the following options configure the benchmark:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-N <number> | signal length |
-r <number> | (for speed bench) number of runs |
-n <number> | (for impulse bench) position of the impulse |
Examples
# Perform Gaussian convolution on the image einstein.png ./gaussian_demo -s 5 -a deriche -K 3 -t 1e-6 einstein.png blurred.png # Compute the L^infty operator error ./gaussian_bench accuracy -N 1000 -s 5 -a deriche -K 3 -t 1e-6
Further examples of using these programs are included in the shell scripts demo.sh and bench.sh.
 1.8.3.1
1.8.3.1